What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Simply put, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the creation of computer systems that can perform tasks that usually require human intelligence. These tasks include learning from experience, recognizing objects and patterns, understanding human language, solving problems, and making decisions.
AI is already impacting daily life across the globe, including in Africa. Examples include financial applications that detect fraudulent transactions through automated decision making, mobile applications that translate local languages, and agricultural tools that analyze drone or satellite images to identify crop diseases through image recognition.
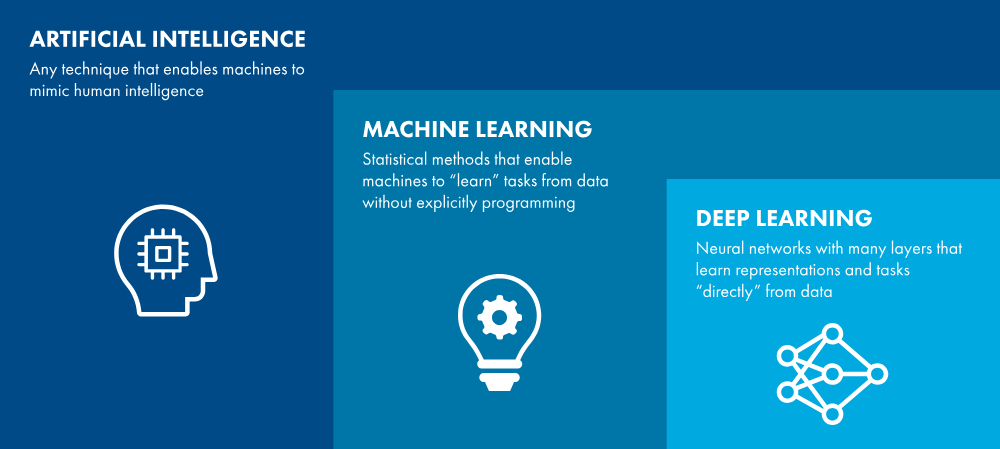
A crucial type of AI and the main focus of this course is Machine Learning (ML). Machine Learning is an approach where computer systems learn from data instead of being explicitly programmed with fixed rules for every situation. The system improves over time by identifying patterns in examples, much like how a child learns by observing and practicing.
Within Machine Learning is a more advanced subset called Deep Learning (DL). Deep Learning uses large amounts of data and multi-layered models inspired by the structure of the human brain to perform complex tasks such as speech recognition, image analysis, and language translation. Many modern AI systems, including voice assistants and facial recognition tools, are powered by deep learning models that rely heavily on high quality annotated data.
Why Annotated Data is the Foundation of AI
If AI learns by example, it needs high-quality, clear examples to learn effectively. This is where annotated data comes in.
Imagine you want to teach an AI system to recognize a mango in a fruit stall photo.
- Raw Data: The original photo of the fruit stall.
- The Problem: The computer sees this photo only as a collection of pixels (numbers) and does not know what a “mango” is.
- The Solution: Annotation: A human (the data annotator) draws a box around the mango in the photo and labels that box, “Mango.” This labeled data is the example the AI needs.
Most successful AI systems today use Supervised Learning. This method requires the human touch of annotation to provide the correct answers. Without a huge library of accurately labeled examples, the AI model cannot learn to recognize patterns and will fail when presented with new, unlabelled data.
Key Concepts and Definitions
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Computer systems designed to simulate human intelligence.
- Machine Learning (ML): A sub-field of AI where systems learn directly from data.
- Supervised Learning: An ML method that requires data to be pre-labeled (annotated) to learn.
- Deep Learning: Subset of machine learning in which multi-layered neural networks learn from vast amounts of data
- Data Annotation: The human led process of labeling raw data (like images or text) to make it understandable for AI models. Also called data labeling.
Practical Implications for Data Annotators: Your job as an annotator is not a side task; it is the most critical starting point for almost every major AI project. You are the teacher providing the foundational knowledge for the AI. The success of a self-driving car in Johannesburg or a health diagnostic tool in Cairo rests squarely on the quality of the data you prepare.
